Somatrogon - Long Acting Growth Hormone
Somatrogon mechanism of action
Fusion of C-terminal peptides (CTPs) from the beta chain of hCG to Somatropin extends half-life by decreasing clearance, and allows once-weekly administration. The mechanism of action is similar to that of hGH.
Somatrogon clinical program development in pediatric growth hormone deficiency overview
Once-Weekly Somatrogon Is Supported by up to 8 years of Efficacy and Safety Data in Pediatric GH Deficiency1-3
COMPLETED
ONGOING
| Study ID | Phase | Title | Enrollment |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP-4-004-E1,2 | 2 | CP-4-004 open-label extension (in the 8th year of treatment) | 48 |
| CP-4-006-E1,7 | 3 | CP-4-006 open-label extension | 212 |
For more information about the different Somatrogon studies – Study design, criteria, endpoints and results
GH, growth hormone; GHD, growth hormone deficiency; O&E, outcomes and evidence.
1. Zadik Z, et al. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab., 2023.3;36(3):261-269. 2. Zelinska N, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2017;102(5):1578-1587. 3. Zadik, Z. et al. (2023) ‘OR21-04 long-term efficacy and safety of once-weekly somatrogon in pediatric subjects with growth hormone deficiency: Results from up to 8 years of somatrogon treatment’, Presented at the Endocrine Society Annual Meeting (ENDO 2023), June 2023. 4. Deal C, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab., 2022.16;107(7):e2717-e2728. 5. Horikawa et al. Horm Res Paediatr 2022. 95(3):275-285 6. Maniatis AK, et al. Journal of the Endocrine Society, 2022.10;6(10):bvac117 7. Wajnrajch M, et al. Poster presented at ENDO Online 2021; March 20-23, 2021.Poster 7129.
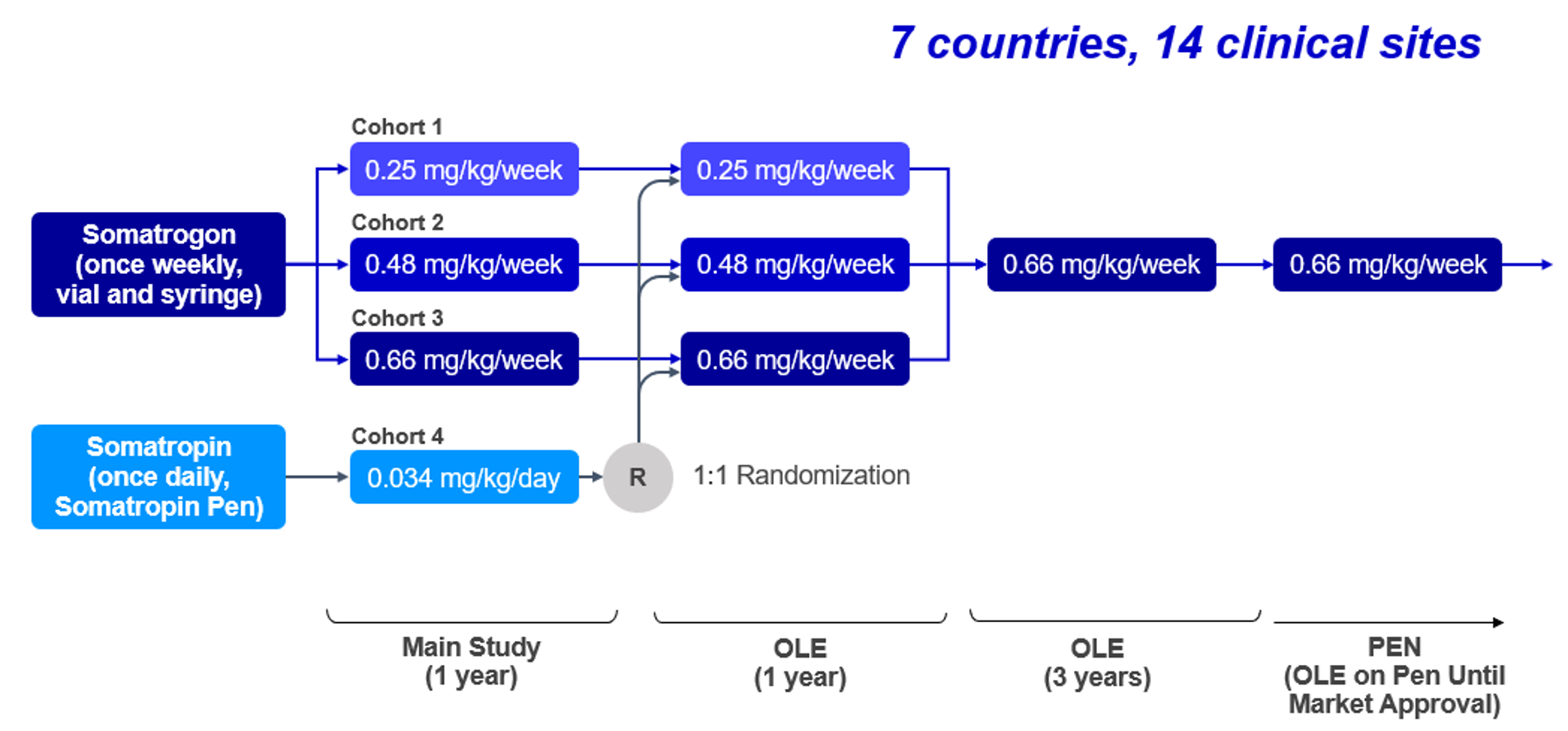
Phase 2 Somatrogon study and the open label extension (OLE)
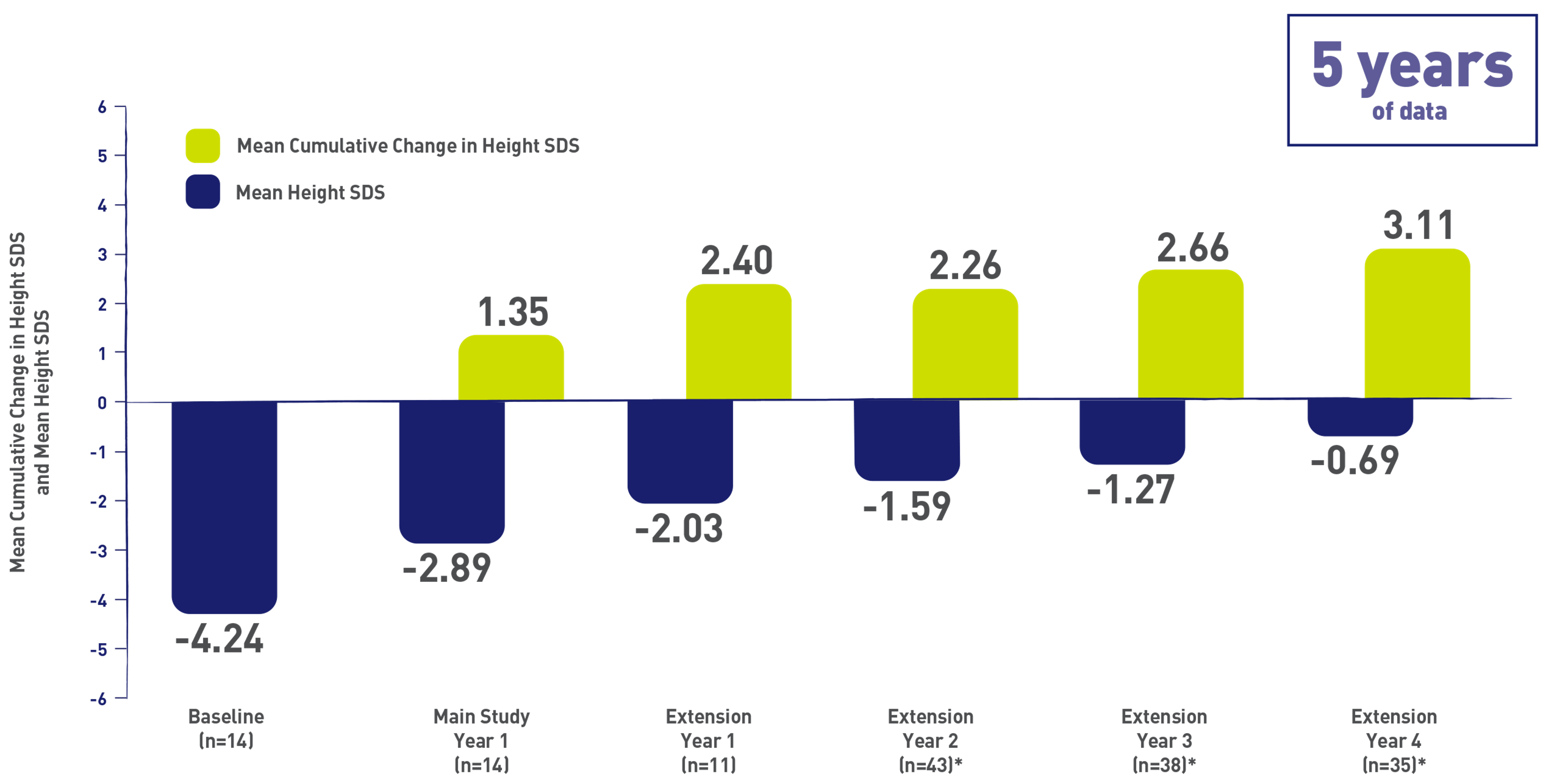
Phase 2 Somatrogon study was a dose-finding, efficacy and safety study in prepubertal children aged 3 years and above with Growth Hormone Deficiency. The phase 2 open label extension has up to 8 years of follow-up. Somatrogon was found to be well tolerated and resulted in sustained improvement in height outcomes1,2.
Primary Efficacy Endpoint: Annual Height Velocity (cm/year ± SD) 1,2
Treatment Difference in Height Velocity at Month 122
OLE, open-label extension; SD, standard deviation; SDS, standard deviation score
*Data shown constitute patients transitioned to pen administration—the majority were after extension year 3. However, 3 patients within this group transitioned after 3 years of treatment, and 1 patient transitioned after 5 years of treatment.3
Most TEAEs were mild or moderate in intensity and the majority was considered unrelated to study treatment. The most commonly reported TEAEs were upper respiratory tract infections (27.1%) and bronchitis (22.9%). 1. Zelinska N, et al. Long-Acting C-Terminal Peptide–Modified hGH (MOD-4023): Results of a Safety and Dose-Finding Study in GHD Children J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2017;102(5):1578-1587. 2. Zadik Z, et al. An open-label extension of a phase 2 dose-finding study of once-weekly somatrogon vs. once-daily Genotropin in children with short stature due to growth hormone deficiency: results following 5 years of treatment. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Feb 3;36(3):261-269. 3. Data on file. REFSMT11833, PFIZER LTD: NGENLA® (somatrogon) CP-4-004 Open Label Extension – Disposition of Subjects.
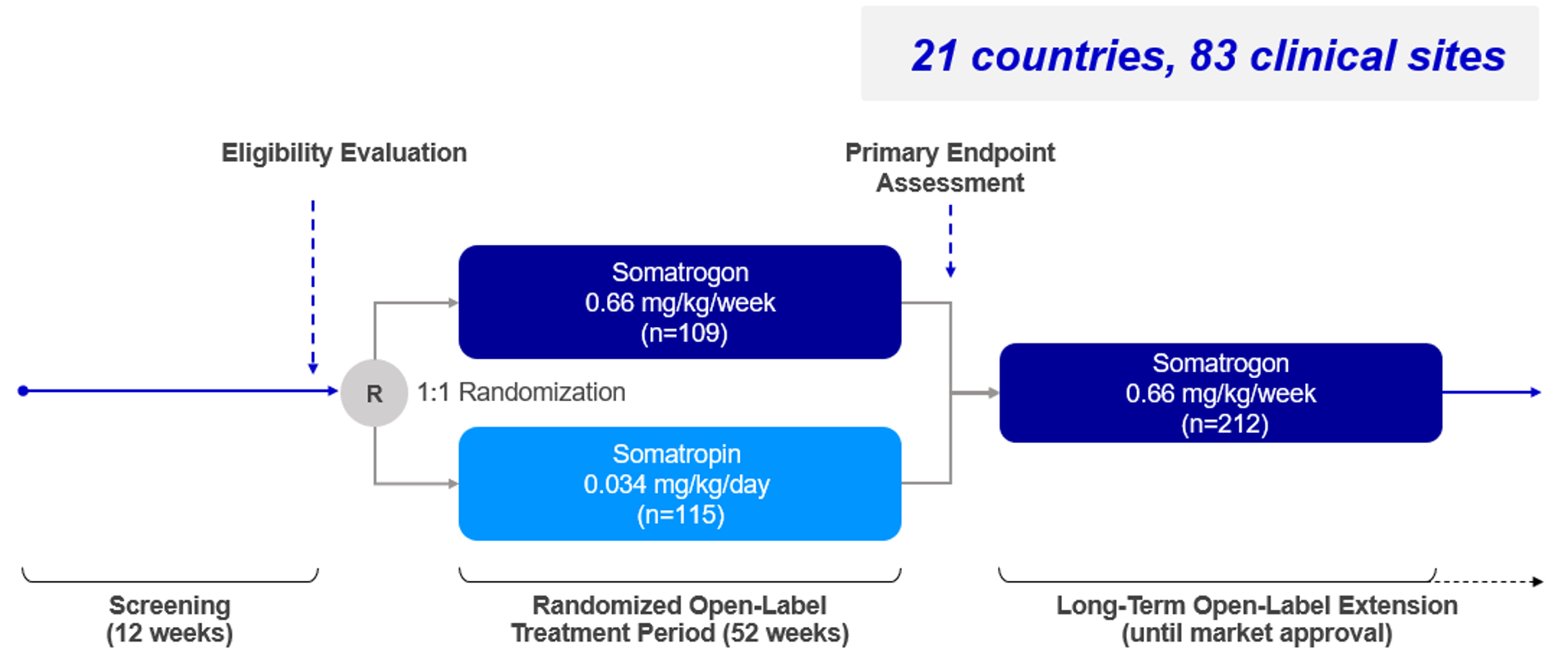
Phase 3 Somatrogon study and the open label extension (OLE)
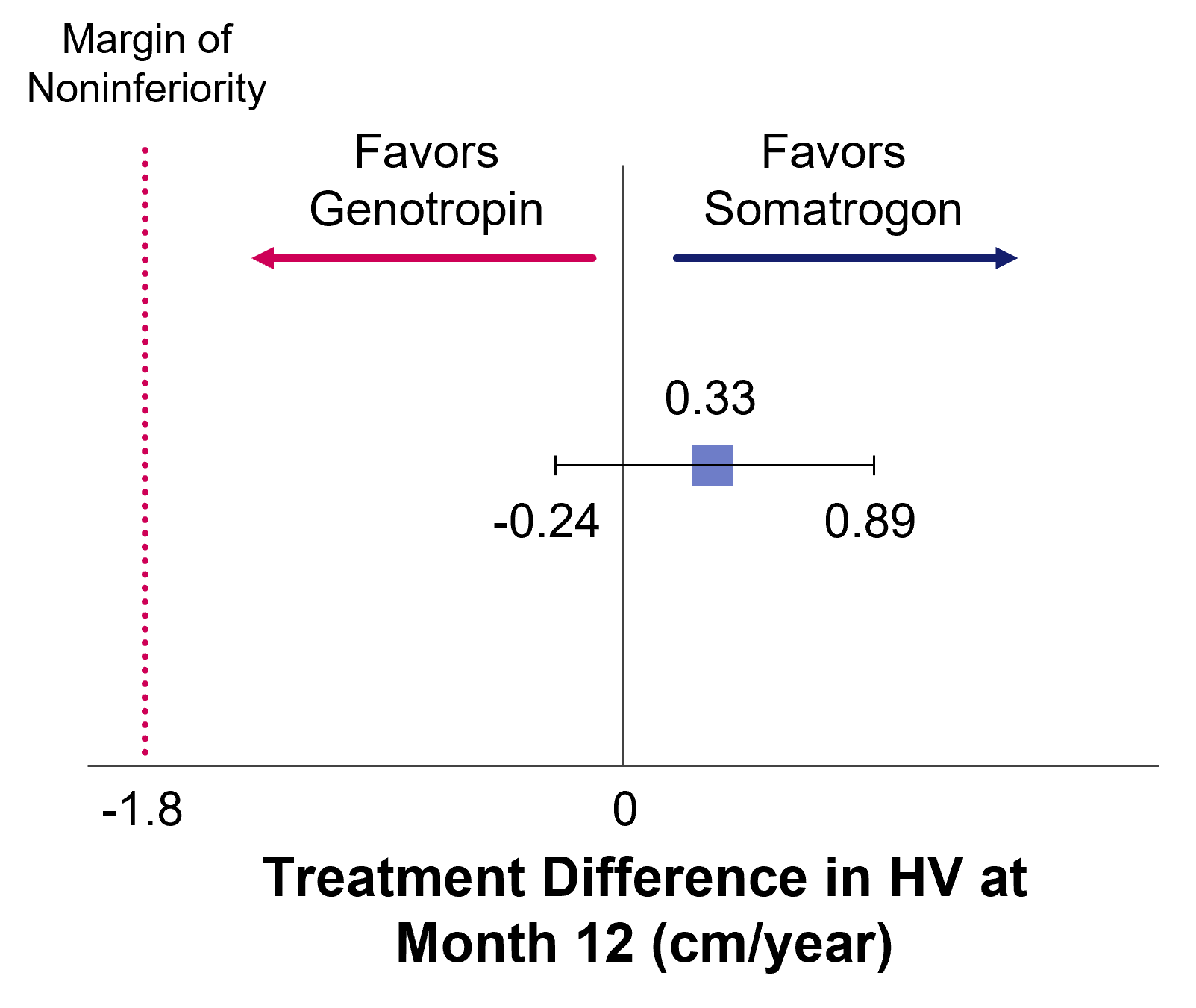
Somatrogon Phase 3 study was a non-inferiority study comparing the efficacy and safety of once-weekly Somatrogon treatment to once-daily somatropin treatment in 224 prepubertal children with growth hormone deficiency over 12 months. The efficacy of once-weekly Somatrogon was noninferior to once-daily somatropin, with similar safety and tolerability profiles. The phase 3 study has an open label extension with several years of follow-up, in which all patients receive somatrogon1.
Primary Endpoint: Annualized HV (cm/year)1
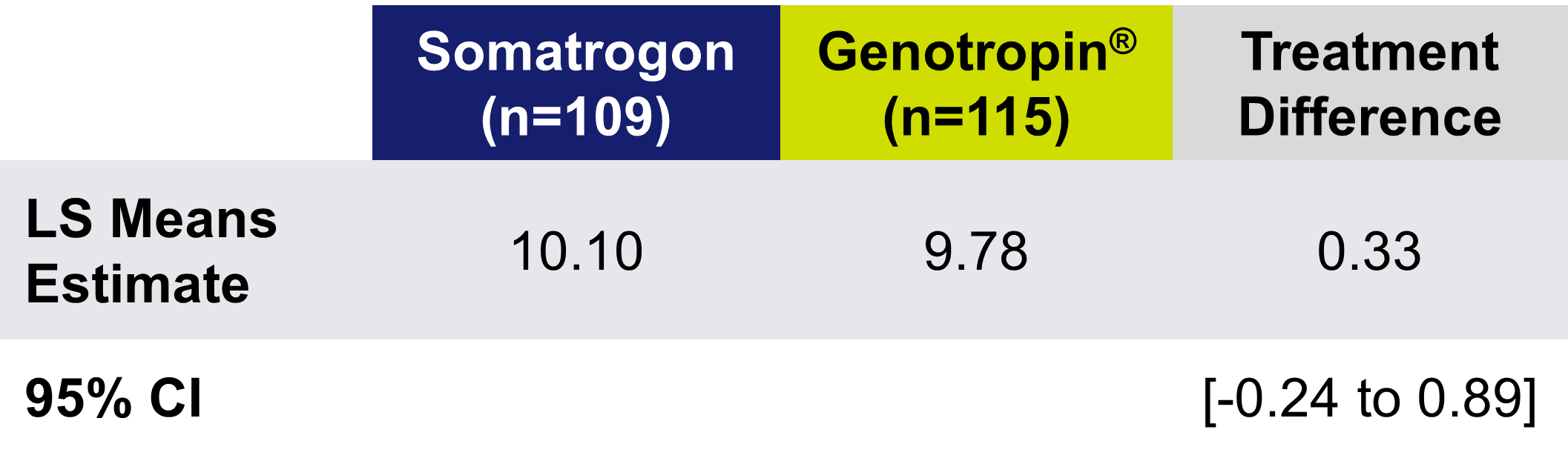
Treatment Difference in HV at Month 12 (cm/year)
Patients Achieved Similar Change in Height SDS to Daily GH With Once-Weekly Somatrogon

LSM, least squares mean; SDS, standard deviation score. Deal C, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab., 2022.16;107(7):e2717-e2728. Used with permission.
TEAEs occurred at a similar rate in both treatment groups, with the majority related to injection site reactions. All-causality TEAEs with ≥ 5% higher incidence in the somatrogon group than in the somatropin group were injection site erythema, injection site pain, and injection site pruritus.
To view an infographic summarizing the phase 3 efficacy and safety data
1. Deal CL, Steelman J, Vlachopapadopoulou E, Stawerska R, Silverman LA, Phillip M, Kim HS, Ko C, Malievskiy O, Cara JF, Roland CL, Taylor CT, Valluri SR, Wajnrajch MP, Pastrak A, Miller BS. Efficacy and Safety of Weekly Somatrogon vs Daily Somatropin in Children With Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Phase 3 Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jun 16;107(7):e2717-e2728.
Treatment Burden Phase 3 Somatrogon study
Somatrogon Treatment Burden phase 3 study compared the treatment burden of once-weekly somatrogon injection to once-daily Somatropin injection in pediatric patients with growth hormone deficiency (GHD). This cross-over study used questionnaires to assess treatment burden from the patient and caregiver perspectives. The results showed that once-weekly somatrogon had significantly lower treatment burden scores than daily somatropin based on assessments of life interference. Somatrogon also provided greater convenience and satisfaction. Both treatments had similar safety profiles1.

Patients and Caregivers Reported Improved (Lower) Life Interference Scores With Once-Weekly Somatrogon Compared to Daily GH1
The LS mean of the overall Life Interference total score was lower for Somatrogon (8.63) compared with Genotropin® (24.13) after 12 weeks of treatment* (The mean difference was -15.49 (95% CI: -19.71 to -11.27))

LS, least squares
*The primary outcome measure is treatment burden assessed as the difference in mean overall Life Interference total score between the weekly and daily injection schedules after 12 weeks of each treatment based on a scale of 1 to 5, with a total score ranging from 7 to 35 (lower score is better).1
Once-Weekly Somatrogon Delivers a Treatment Experience Favored by Patients and Caregivers**

PGIS-DA, Patient Global Impression Severity-Impact on Daily Activities.
**Caregivers completed the assessment of signs for children under 8 years of age.
The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) for Somatropin and somatrogon was 44.2% and 54.0%, respectively. No severe or serious AEs were reported.
Watch Dr. Maniatis, lead Author of the phase 3 treatment burden study, summarize the study
1. Maniatis AK, Carakushansky M, Galcheva S, Prakasam G, Fox LA, Dankovcikova A, Loftus J, Palladino AA, de Los Angeles Resa M, Turich Taylor C, Dattani MT, Lebl J. Treatment Burden of Weekly Somatrogon vs Daily Somatropin in Children With Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Randomized Study. . J Endocr Soc. 2022 Sep 10;6(10):bvac117.
IGF-1 Monitoring During Somatrogon Treatment in Children with GHD
Somatrogon dose may be adjusted as necessary, based on growth velocity, adverse reactions, body weight and serum insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) concentrations. When monitoring for IGF-1, samples should always be drawn 4 days after the prior dose. Dose adjustments should be targeted to achieve average IGF-1 standard deviation score (SDS) levels in the normal range, i.e. between -2 and +2 (preferably close to 0 SDS).
In this section you will be able to learn more about the rational for IGF-1 monitoring recommendations with Somatrogon and find a conversion table for IGF-1 samples taken on different times after the prior dose.
IGF-1 Samples Should be Drawn on Day 4 After Dose Administration1–5
Conceptual Representation of Somatorogon PD Profile1,3

Somatrogon and IGF-1 Monitoring in Clinical Practice2,6,7
Figures were adapted from Deal CL et al. 20229 and Ngenla, Prescribing information, Israel3.
BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; GHD, growth hormone deficiency; IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor 1; LAGH, long acting growth hormone; LSM, least square mean; OLE, open label extension; rhGH, recombinant human growth hormone; SDS, standard deviation score.
IGF-1 Was Measured on Different Days During the Global Phase 3 Somatrogon Clinical Trial9-11
The majority of IGF-1 samples were taken between days 2 - 4

- PK/PD modeling studies were developed and further validated in the global phase 3 study
- This allowed determination of the appropriate time after somatrogon dosing to predict mean and peak IGF-1 SDS
IGF-1=insulin-like growth factor 1; PD=pharmacodynamic; PK=pharmacokinetic; SDS=standard deviation score.
The blue line is a smoother (Supersmoother®); vertical lines delimit days. Within each bin (and for all samples), the total number of samples and the percent of samples > +2.0, < 0.0, and < -2.0 are displayed. Two samples obtained after day 12 are displayed to the right as red integers indicating their time-after-dose.
Simplified summary of adjustments required to be applied to measured IGF-1and IGF-1SDS

Data on file
Example: Correcting for a Day 2 Sample

Data on file
For further information on IGF-1 profile and monitoring
1.Kildemoes RJ et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021;106:567–576; 2. Ngenla, Prescribing information, Israel. 3. Chong YM et al. Anticancer Res 2007;27:1617–1624; 4. Laron Z. Mol Pathol2001;54:311–316; 5. Blum WF et al. Endocr Connect 2018;7:R212–R222; 6. Kos S et al. Eur J Endocrinol 2019;181:L1–L4; 7. Chanson P et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016;101:3450–3458; 8. Bidlingmaier M et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021;106:e2367–e23694; 9. Deal CL et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107:e2717–e2728; 10. Fisher DM, et al. Presented at: International Congress of Endocrinology; February 24‒28, 2021 (virtual). 2. Fisher DM, et al. Horm Res Paediatr. 2017;87:324‐332.
Somatrogon mechanism of action
Fusion of C-terminal peptides (CTPs) from the beta chain of hCG to Somatropin extends half-life by decreasing clearance, and allows once-weekly administration. The mechanism of action is similar to that of hGH.
Somatrogon clinical program development in pediatric growth hormone deficiency overview
Once-Weekly Somatrogon Is Supported by up to 8 years of Efficacy and Safety Data in Pediatric GH Deficiency1-3
COMPLETED
ONGOING
| Study ID | Phase | Title | Enrollment |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP-4-004-E1,2 | 2 | CP-4-004 open-label extension (in the 8th year of treatment) | 48 |
| CP-4-006-E1,7 | 3 | CP-4-006 open-label extension | 212 |
For more information about the different Somatrogon studies – Study design, criteria, endpoints and results
GH, growth hormone; GHD, growth hormone deficiency; O&E, outcomes and evidence.
1. Zadik Z, et al. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab., 2023.3;36(3):261-269. 2. Zelinska N, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2017;102(5):1578-1587. 3. Zadik, Z. et al. (2023) ‘OR21-04 long-term efficacy and safety of once-weekly somatrogon in pediatric subjects with growth hormone deficiency: Results from up to 8 years of somatrogon treatment’, Presented at the Endocrine Society Annual Meeting (ENDO 2023), June 2023. 4. Deal C, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab., 2022.16;107(7):e2717-e2728. 5. Horikawa et al. Horm Res Paediatr 2022. 95(3):275-285 6. Maniatis AK, et al. Journal of the Endocrine Society, 2022.10;6(10):bvac117 7. Wajnrajch M, et al. Poster presented at ENDO Online 2021; March 20-23, 2021.Poster 7129.
Phase 2 Somatrogon study and the open label extension (OLE)
Phase 2 Somatrogon study was a dose-finding, efficacy and safety study in prepubertal children aged 3 years and above with Growth Hormone Deficiency. The phase 2 open label extension has up to 8 years of follow-up. Somatrogon was found to be well tolerated and resulted in sustained improvement in height outcomes1,2.

Primary Efficacy Endpoint: Annual Height Velocity (cm/year ± SD) 1,2
Treatment Difference in Height Velocity at Month 122

OLE, open-label extension; SD, standard deviation; SDS, standard deviation score
*Data shown constitute patients transitioned to pen administration—the majority were after extension year 3. However, 3 patients within this group transitioned after 3 years of treatment, and 1 patient transitioned after 5 years of treatment.3
Most TEAEs were mild or moderate in intensity and the majority was considered unrelated to study treatment. The most commonly reported TEAEs were upper respiratory tract infections (27.1%) and bronchitis (22.9%). 1. Zelinska N, et al. Long-Acting C-Terminal Peptide–Modified hGH (MOD-4023): Results of a Safety and Dose-Finding Study in GHD Children J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2017;102(5):1578-1587. 2. Zadik Z, et al. An open-label extension of a phase 2 dose-finding study of once-weekly somatrogon vs. once-daily Genotropin in children with short stature due to growth hormone deficiency: results following 5 years of treatment. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Feb 3;36(3):261-269. 3. Data on file. REFSMT11833, PFIZER LTD: NGENLA® (somatrogon) CP-4-004 Open Label Extension – Disposition of Subjects.
Phase 3 Somatrogon study and the open label extension (OLE)
Somatrogon Phase 3 study was a non-inferiority study comparing the efficacy and safety of once-weekly Somatrogon treatment to once-daily somatropin treatment in 224 prepubertal children with growth hormone deficiency over 12 months. The efficacy of once-weekly Somatrogon was noninferior to once-daily somatropin, with similar safety and tolerability profiles. The phase 3 study has an open label extension with several years of follow-up, in which all patients receive somatrogon1.

Primary Endpoint: Annualized HV (cm/year)1

Treatment Difference in HV at Month 12 (cm/year)

Patients Achieved Similar Change in Height SDS to Daily GH With Once-Weekly Somatrogon

LSM, least squares mean; SDS, standard deviation score. Deal C, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab., 2022.16;107(7):e2717-e2728. Used with permission.
TEAEs occurred at a similar rate in both treatment groups, with the majority related to injection site reactions. All-causality TEAEs with ≥ 5% higher incidence in the somatrogon group than in the somatropin group were injection site erythema, injection site pain, and injection site pruritus.
To view an infographic summarizing the phase 3 efficacy and safety data
1. Deal CL, Steelman J, Vlachopapadopoulou E, Stawerska R, Silverman LA, Phillip M, Kim HS, Ko C, Malievskiy O, Cara JF, Roland CL, Taylor CT, Valluri SR, Wajnrajch MP, Pastrak A, Miller BS. Efficacy and Safety of Weekly Somatrogon vs Daily Somatropin in Children With Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Phase 3 Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jun 16;107(7):e2717-e2728.
Treatment Burden Phase 3 Somatrogon study
Somatrogon Treatment Burden phase 3 study compared the treatment burden of once-weekly somatrogon injection to once-daily Somatropin injection in pediatric patients with growth hormone deficiency (GHD). This cross-over study used questionnaires to assess treatment burden from the patient and caregiver perspectives. The results showed that once-weekly somatrogon had significantly lower treatment burden scores than daily somatropin based on assessments of life interference. Somatrogon also provided greater convenience and satisfaction. Both treatments had similar safety profiles1.

Patients and Caregivers Reported Improved (Lower) Life Interference Scores With Once-Weekly Somatrogon Compared to Daily GH1
The LS mean of the overall Life Interference total score was lower for Somatrogon (8.63) compared with Genotropin® (24.13) after 12 weeks of treatment* (The mean difference was -15.49 (95% CI: -19.71 to -11.27))

LS, least squares
*The primary outcome measure is treatment burden assessed as the difference in mean overall Life Interference total score between the weekly and daily injection schedules after 12 weeks of each treatment based on a scale of 1 to 5, with a total score ranging from 7 to 35 (lower score is better).1
Once-Weekly Somatrogon Delivers a Treatment Experience Favored by Patients and Caregivers**

PGIS-DA, Patient Global Impression Severity-Impact on Daily Activities.
**Caregivers completed the assessment of signs for children under 8 years of age.
The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) for Somatropin and somatrogon was 44.2% and 54.0%, respectively. No severe or serious AEs were reported.
Watch Dr. Maniatis, lead Author of the phase 3 treatment burden study, summarize the study
1. Maniatis AK, Carakushansky M, Galcheva S, Prakasam G, Fox LA, Dankovcikova A, Loftus J, Palladino AA, de Los Angeles Resa M, Turich Taylor C, Dattani MT, Lebl J. Treatment Burden of Weekly Somatrogon vs Daily Somatropin in Children With Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Randomized Study. . J Endocr Soc. 2022 Sep 10;6(10):bvac117.
IGF-1 Monitoring During Somatrogon Treatment in Children with GHD
Somatrogon dose may be adjusted as necessary, based on growth velocity, adverse reactions, body weight and serum insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) concentrations. When monitoring for IGF-1, samples should always be drawn 4 days after the prior dose. Dose adjustments should be targeted to achieve average IGF-1 standard deviation score (SDS) levels in the normal range, i.e. between -2 and +2 (preferably close to 0 SDS).
In this section you will be able to learn more about the rational for IGF-1 monitoring recommendations with Somatrogon and find a conversion table for IGF-1 samples taken on different times after the prior dose.
IGF-1 Samples Should be Drawn on Day 4 After Dose Administration1–5
Conceptual Representation of Somatorogon PD Profile1,3

Somatrogon and IGF-1 Monitoring in Clinical Practice2,6,7
Figures were adapted from Deal CL et al. 20229 and Ngenla, Prescribing information, Israel3.
BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; GHD, growth hormone deficiency; IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor 1; LAGH, long acting growth hormone; LSM, least square mean; OLE, open label extension; rhGH, recombinant human growth hormone; SDS, standard deviation score.
IGF-1 Was Measured on Different Days During the Global Phase 3 Somatrogon Clinical Trial9-11
The majority of IGF-1 samples were taken between days 2 - 4

- PK/PD modeling studies were developed and further validated in the global phase 3 study
- This allowed determination of the appropriate time after somatrogon dosing to predict mean and peak IGF-1 SDS
IGF-1=insulin-like growth factor 1; PD=pharmacodynamic; PK=pharmacokinetic; SDS=standard deviation score.
The blue line is a smoother (Supersmoother®); vertical lines delimit days. Within each bin (and for all samples), the total number of samples and the percent of samples > +2.0, < 0.0, and < -2.0 are displayed. Two samples obtained after day 12 are displayed to the right as red integers indicating their time-after-dose.
Simplified summary of adjustments required to be applied to measured IGF-1and IGF-1SDS

Data on file
Example: Correcting for a Day 2 Sample

Data on file
For further information on IGF-1 profile and monitoring
1.Kildemoes RJ et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021;106:567–576; 2. Ngenla, Prescribing information, Israel. 3. Chong YM et al. Anticancer Res 2007;27:1617–1624; 4. Laron Z. Mol Pathol2001;54:311–316; 5. Blum WF et al. Endocr Connect 2018;7:R212–R222; 6. Kos S et al. Eur J Endocrinol 2019;181:L1–L4; 7. Chanson P et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016;101:3450–3458; 8. Bidlingmaier M et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021;106:e2367–e23694; 9. Deal CL et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107:e2717–e2728; 10. Fisher DM, et al. Presented at: International Congress of Endocrinology; February 24‒28, 2021 (virtual). 2. Fisher DM, et al. Horm Res Paediatr. 2017;87:324‐332.
For further safety information please refer to the latest SOMATROGON 20 MG/ML or SOMATROGON 50 MG/ML prescribing information.